Tchaikovsky
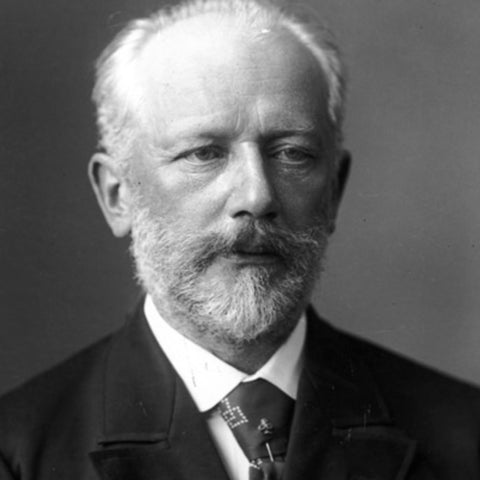
Although musically precocious, Tchaikovsky was educated for a career as a civil servant. There was scant opportunity for a musical career in Russia at that time and no system of public music education. When an opportunity for such an education arose, he entered the nascent Saint Petersburg Conservatory, from which he graduated in 1865. The formal Western-oriented teaching he received there set him apart from composers of the contemporary nationalist movement embodied by the Russian composers of The Five, with whom his professional relationship was mixed. Tchaikovsky's training set him on a path to reconcile what he had learned with the native musical practices to which he had been exposed from childhood. From this reconciliation, he forged a personal but unmistakably Russian style—a task that did not prove easy. The principles that governed melody, harmony and other fundamentals of Russian music ran completely counter to those that governed Western European music; this seemed to defeat the potential for using Russian music in large-scale Western composition or for forming a composite style, and it caused personal antipathies that dented Tchaikovsky's self-confidence. Russian culture exhibited a split personality, with its native and adopted elements having drifted apart increasingly since the time of Peter the Great. This resulted in uncertainty among the intelligentsia about the country's national identity—an ambiguity mirrored in Tchaikovsky's career.
Despite his many popular successes, Tchaikovsky's life was punctuated by personal crises and depression. Contributory factors included his early separation from his mother for boarding school followed by his mother's early death, the death of his close friend and colleague Nikolai Rubinstein, and the collapse of the one enduring relationship of his adult life, which was his 13-year association with the wealthy widow Nadezhda von Meck. His homosexuality, which he kept private, has traditionally also been considered a major factor, though some musicologists now downplay its importance. Tchaikovsky's sudden death at the age of 53 is generally ascribed to cholera; there is an ongoing debate as to whether cholera was indeed the cause of death, and whether it was accidental or self-inflicted.
While his music has remained popular among audiences, critical opinions were initially mixed. Some Russians did not feel it was sufficiently representative of native musical values and expressed suspicion that Europeans accepted the music for its Western elements. In an apparent reinforcement of the latter claim, some Europeans lauded Tchaikovsky for offering music more substantive than base exoticism and said he transcended stereotypes of Russian classical music. Others dismissed Tchaikovsky's music as "lacking in elevated thought," according to longtime New York Times music critic Harold C. Schonberg, and derided its formal workings as deficient because they did not stringently follow Western principles.
Tchaikovsky
TCHAIKOVSKY Symphony No. 4
SAINT-SAËNS Danse Macabre
BIZET Petite Suite
Music by Chopin, Meyerbeer, Mascagni, Schubert & many more
Studio and Live Recordings, 1920 - 1925
Total duration: 2hr 20:22
Alfred Cortot
Jesse Crawford
Giuseppe De Luca
Art Gillham
Mischa Levitzky
Margarete Matzenauer
Landon Ronald
Leopold Stokowski
and many more
TCHAIKOVSKY 1812 Overture
TCHAIKOVSKY Capriccio Italien
TCHAIKOVSKY Marche Slave
Recorded 1958
Total duration: 39:06
London Symphony Orchestra
conducted by Kenneth Alwyn
with The Band of H.M. Grenadier Guards
Director of Music Major F. J. Harris MBE
TCHAIKOVSKY Francesca da Rimini
TCHAIKOVSKY Symphony No. 5
TCHAIKOVSKY Symphony No. 6 'Pathétique' (2nd & 3rd mvts)
Studio recordings, 1939/40 & 1915
Total duration: 76:15
London Philharmonic Orchestra
Beecham Symphony Orchestra
conducted by Sir Thomas Beecham
NICOLAI The Merry Wives of Windsor: Overture
ELGAR Serenade for Strings
HANDEL-BEECHAM Love in Bath: The Great Elopement
DELIUS The Walk to the Paradise Garden
J. STRAUSS II Voices of Spring
WAGNER Götterdämmerung: Siegfried’s Funeral March
SIBELIUS Pelléas et Mélisande Suite: The Death of Mélisande
MOZART Divertimento, K 131: Adagio
SCHUBERT Symphony No. 8, “Unfinished.”
TCHAIKOVSKY Serenade in C: Elegie
BERLIOZ Les Troyens: Trojan March
MOZART Symphony No. 31
HANDEL-BEECHAM Piano Concerto
CHABRIER España
MOZART The Impressario - Overture
SAINT-SAENS Omphale’s Spinning Wheel
BERLIOZ The Trojans - Royal Hunt and Storm
BERLIOZ Hungarian March
Recorded in 1945
Sir Thomas Beecham, conductor
Blue Network Symphony Orchestra
SIBELIUS Pelléas et Mélisande Suite: The Death of Mélisande
MOZART Divertimento, K 131: Adagio
SCHUBERT Symphony No. 8, “Unfinished.”
TCHAIKOVSKY Serenade in C: Elegie
BERLIOZ Les Troyens: Trojan March
Live broadcast on ABC/Blue Network, 4pm, 14 April 1945
Total duration: 57:50
Blue Network Symphony Orchestra
DEBUSSY Petite Suite
OFFENBACH Tales of Hoffman
STRAVINSKY The Firebird - Suite
TCHAIKOVSKY Symphony No. 6 "Pathétique"
and many more
Studio recordings, 1910-1918
Total duration: 2hr 32:36 (CD) or 2hr 39:21 (download)
Beecham Symphony Orchestra
conducted by Sir Thomas Beecham
-
Previous
- Page 1 of 17
- Next






